Introduction
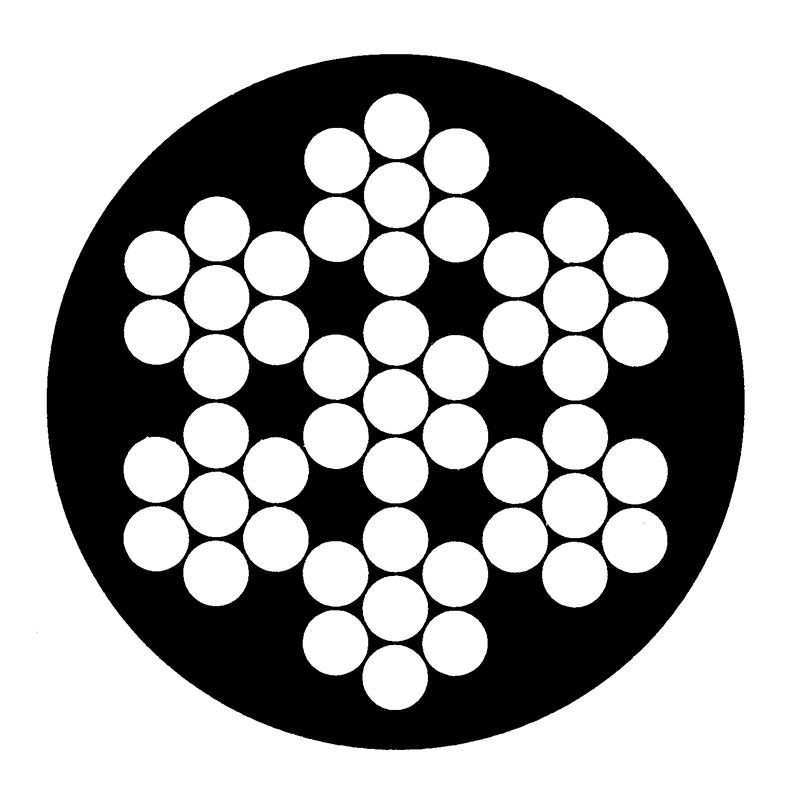
WIRE ROPE, commonly known as steel wire rope, is a versatile and essential component in various industrial and construction applications. It consists of multiple strands of metal wires twisted together to form a strong, flexible, and durable rope capable of handling heavy loads.
Understanding WIRE ROPE is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and longevity in its usage. From lifting and hoisting operations to structural support and marine applications, WIRE ROPE plays a vital role in daily operations where strength and reliability are paramount.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of WIRE ROPE, covering installation techniques, maintenance tips, safety standards, corrosion prevention, and performance analysis. By the end, readers will gain practical knowledge to select, use, and maintain WIRE ROPE effectively, maximizing its lifespan and performance in demanding environments.
WIRE ROPE Installation Guide
Proper installation of WIRE ROPE is critical to ensure its safety, performance, and longevity. Incorrect installation can lead to premature wear, reduced strength, and even accidents. The following guide provides step-by-step instructions for installing WIRE ROPE effectively.
1. Preparation Before Installation
- Inspect the WIRE ROPE for any visible damage, such as broken strands or corrosion.
- Ensure all tools and equipment are clean, well-maintained, and suitable for handling steel ropes.
- Measure the required length accurately and account for terminations and fittings.
2. Installation Steps
- Positioning: Carefully route the WIRE ROPE along the intended path without sharp bends or twists.
- Securing Ends: Attach appropriate end fittings, such as sockets, clamps, or thimbles, ensuring they are tightly secured.
- Tensioning: Gradually apply tension to the WIRE ROPE, avoiding sudden loads that could cause kinks or uneven stress.
- Alignment: Check that the rope runs smoothly along pulleys, sheaves, or drums, and adjust as necessary to prevent friction and wear.
3. Common Installation Mistakes to Avoid
- Twisting or kinking the rope during handling.
- Overloading the rope before it has been properly seated in fittings.
- Ignoring recommended bending radii for pulleys and drums.
WIRE ROPE Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance of WIRE ROPE is essential for safety, performance, and longevity. Regular inspection and care can prevent unexpected failures and extend the life of the rope.
1. Routine Inspection
- Visual Check: Examine the WIRE ROPE for broken wires, corrosion, kinks, or abrasion.
- Flexibility Test: Bend the rope gently to detect stiffness or internal damage.
- End Fittings: Inspect sockets, clamps, and thimbles for wear or loosening.
2. Lubrication and Cleaning
- Apply appropriate lubricants to reduce friction between strands and prevent corrosion.
- Clean the rope regularly to remove dirt, debris, and moisture that may accelerate wear.
3. Storage Guidelines
- Store WIRE ROPE in a dry, well-ventilated area.
- Avoid direct contact with chemicals or surfaces that may cause abrasion or corrosion.
- Coil the rope properly to prevent kinks and maintain its structural integrity.
4. Recommended Maintenance Intervals
The maintenance frequency depends on usage conditions, load, and environment. Heavy-duty or outdoor applications may require more frequent inspection and lubrication.
WIRE ROPE Maintenance Comparison Table
| Parameter | Light-Duty Use | Medium-Duty Use | Heavy-Duty/Outdoor Use |
| Inspection Frequency | Monthly | Bi-weekly | Weekly |
| Lubrication Interval | Every 3–6 months | Every 1–3 months | Every 2–4 weeks |
| Cleaning Requirement | Basic cleaning | Moderate cleaning | Thorough cleaning |
| Storage Condition | Indoor, dry | Indoor, ventilated | Covered, dry, ventilated |
| Replacement Consideration | Minor wear | Noticeable wear | Significant wear or broken wires |
WIRE ROPE Safety Standards
Adhering to proper safety standards is essential when using WIRE ROPE in any application. Safety standards help ensure that the rope can handle the intended loads without failure and reduce the risk of accidents.
1. Key Safety Considerations
- Load Capacity: Never exceed the rated working load limit (WLL) of the WIRE ROPE.
- Inspection Before Use: Always inspect for broken strands, corrosion, kinks, or other damage before operation.
- Proper Termination: Ensure end fittings, clamps, and sockets are correctly installed and secured.
- Avoid Abrasion and Twisting: Use sheaves and drums with appropriate diameters to prevent excessive wear.
2. Common Safety Standards
- Breaking Strength vs. Working Load: The WIRE ROPE’s working load should typically be 1/5 to 1/6 of its minimum breaking strength (MBS) to maintain a safe safety factor.
- Bend Radius: The rope must maintain proper bend radius over pulleys or sheaves to prevent internal damage.
- Environmental Considerations: Protective measures should be taken for corrosive or extreme environments, including lubrication or coating.
WIRE ROPE Safety Standard Comparison Table
| Standard Aspect | Requirement | Recommended Practice |
| Working Load Limit (WLL) | ≤ 1/5 to 1/6 of minimum breaking strength | Do not exceed the rated load |
| Inspection Frequency | Before each use (high-risk), monthly (normal) | Regularly document inspections |
| Bend Radius | ≥ 20× rope diameter (for general use) | Use larger sheaves to reduce stress |
| End Fittings | Properly secured and tightened | Use recommended fittings and torque |
| Environmental Protection | Corrosion prevention if exposed to moisture or chemicals | Apply lubrication or coating |
WIRE ROPE Corrosion Prevention
Corrosion is one of the primary factors that reduce the lifespan and safety of WIRE ROPE. Proper prevention methods are essential, especially in environments exposed to moisture, saltwater, or chemicals.
1. Common Types of Corrosion
- Surface Rust: Occurs when steel wires are exposed to moisture.
- Pitting Corrosion: Localized damage leading to weak spots.
- Galvanic Corrosion: Happens when WIRE ROPE comes into contact with dissimilar metals in a conductive environment.
2. Prevention Methods
- Lubrication: Regularly apply appropriate lubricants to reduce moisture contact and friction between strands.
- Protective Coatings: Galvanized or coated WIRE ROPE can resist oxidation and corrosion.
- Environmental Control: Store ropes in dry, ventilated areas away from chemicals and saltwater exposure.
- Regular Inspection: Identify early signs of corrosion and replace affected sections promptly.
WIRE ROPE Corrosion Prevention Comparison Table
| Method | Advantages | Recommended Use Case |
| Lubrication | Reduces friction, prevents moisture buildup | General indoor and outdoor use |
| Galvanized or Coated Rope | Resistant to surface rust | Outdoor, marine, or high-humidity areas |
| Dry Storage | Minimizes exposure to corrosive elements | Long-term storage |
| Regular Inspection | Early detection of corrosion | All usage environments |
| Avoid Dissimilar Metals | Prevents galvanic corrosion | Situations where rope contacts other metals |
WIRE ROPE Tensile Strength and Performance Analysis
Understanding the tensile strength and overall performance of WIRE ROPE is essential for selecting the right rope for specific applications. Tensile strength indicates the maximum load the rope can withstand before failure, while other performance metrics such as flexibility and abrasion resistance impact its usability.
1. Key Performance Metrics
- Minimum Breaking Strength (MBS): Maximum load before the rope fails.
- Working Load Limit (WLL): Safe operating load, usually 1/5 to 1/6 of MBS.
- Elongation: Degree to which the rope stretches under load.
- Flexibility: Ease of bending over pulleys or sheaves.
- Resistance to Wear: Ability to withstand abrasion, twisting, and environmental stress.
2. Factors Affecting Performance
- Rope construction (strand type, number of wires, core type)
- Diameter of the rope
- Environmental conditions (corrosion, temperature, chemicals)
- Load type (static vs dynamic)
WIRE ROPE Tensile Strength Comparison Table
| Rope Type | Diameter (mm) | Minimum Breaking Strength (tons) | Working Load Limit (tons) | Flexibility | Typical Use Case |
| 6×19 IWRC | 10 | 12.5 | 2.5 | Moderate | General lifting, cranes |
| 6×36 FC | 12 | 18 | 3.6 | High | Hoisting, winches |
| 8×19 IWRC | 16 | 32 | 6.4 | Moderate | Heavy lifting, construction |
| 6×25 Seale | 20 | 45 | 9 | Low | Marine, structural applications |
| 6×36 IWRC | 24 | 65 | 13 | High | Mining, heavy-duty cranes |
Summary and Practical Recommendations
WIRE ROPE is an essential component in numerous industrial, construction, and marine applications. From lifting and hoisting to structural support, understanding the properties, proper usage, and maintenance of WIRE ROPE is critical for safety and efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Installation: Proper installation ensures that WIRE ROPE performs safely under load. Avoid twisting, kinking, or exceeding bend radius limits.
- Maintenance: Regular inspection, cleaning, and lubrication extend the rope’s lifespan and prevent unexpected failures.
- Safety Standards: Adhering to working load limits, bend radius recommendations, and environmental precautions minimizes risks.
- Corrosion Prevention: Lubrication, protective coatings, proper storage, and avoiding contact with dissimilar metals prevent corrosion.
- Performance Analysis: Understanding tensile strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance ensures the selection of WIRE ROPE suited for specific tasks.
Practical Recommendations for WIRE ROPE Users
| Area | Recommendation |
| Installation | Follow step-by-step installation guides and inspect fittings |
| Maintenance | Schedule inspections based on duty and environment |
| Safety Compliance | Use WLL ≤ 1/5 of minimum breaking strength |
| Corrosion Prevention | Apply lubrication, use coated ropes, store in dry areas |
| Performance Monitoring | Regularly review load history and rope condition |
FAQ
1. What types of WIRE ROPE are available and how do I choose the right one?
WIRE ROPE comes in various constructions, diameters, and materials, each suited for specific applications such as lifting, hoisting, or structural support. When selecting WIRE ROPE, consider factors like tensile strength, flexibility, corrosion resistance, and working load limits. For high-quality and reliable options, Shanghai TCH Metals & Machinery Co., Ltd. offers a wide range of WIRE ROPE products, backed by decades of expertise in manufacturing and distribution, ensuring that customers receive ropes tailored to their operational needs.
2. How should WIRE ROPE be maintained to ensure safety and longevity?
Regular inspection, lubrication, proper storage, and adherence to safety standards are essential for maintaining WIRE ROPE. Inspect the rope for broken strands, corrosion, or kinks, and lubricate it to reduce friction and prevent wear. Shanghai TCH Metals & Machinery Co., Ltd. not only provides superior WIRE ROPE products but also offers expert guidance and technical support on maintenance practices, helping clients maximize safety and extend the service life of their ropes.
3. What makes Shanghai TCH Metals & Machinery Co., Ltd. a trusted provider of WIRE ROPE and related products?
Shanghai TCH Metals & Machinery Co., Ltd. is a leading company specializing in the manufacturing and distribution of metals and machinery, including chains, tire chains, slings, WIRE ROPE, cargo controls, and rigging hardware. Established in 2001, the company has over two decades of experience delivering high-quality products worldwide, with strong market presence in North America, Europe, and Japan. Equipped with state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities and a dedicated team of professionals, Shanghai TCH Metals & Machinery Co., Ltd. is committed to providing superior products and exceptional service, making it the premier choice for businesses seeking reliable WIRE ROPE solutions.

 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語