I. Fundamentals of Industrial Transmission: Positioning the Japanese Standard Chain
A. Introduction to Core Concepts
Chains are the unsung heroes of heavy industry, serving a critical dual role in nearly all automated and mechanized processes: power transmission and material conveyance. In transmission, they translate rotational power from a motor or gearbox into usable motion, ensuring precision timing and efficient power transfer across machinery. In conveyance, they form the backbone of conveyor systems, moving everything from small components to large assemblies across a factory floor. The efficiency, safety, and longevity of entire industrial systems fundamentally depend on the quality and adherence to strict specifications of these components.
B. Defining the Product Category: What is a JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain?
The JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain is a distinct product category defined by its adherence to the rigorous technical requirements set forth by the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS). It is not just any chain; it is a precision transmission component manufactured under strict quality control to meet the dimensional and performance criteria outlined in the relevant JIS standards, such as JIS B 1801 (for roller chains). This certification ensures that the chain possesses specific characteristics in terms of pitch, roller diameter, and tensile strength, guaranteeing reliable performance and essential interchangeability within any equipment built to Japanese standards.
C. Relationship with International Standards
While the JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain is defined by national Japanese specifications, its underlying principles are closely aligned with global norms. The Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) are often harmonized with the standards set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Therefore, a chain manufactured to the JIS standard typically meets or exceeds the basic requirements of the equivalent ISO standard. This compatibility means that the Japanese standard chain is widely trusted and applicable in machinery used globally, ensuring its seamless integration into diverse international manufacturing and automation environments.
II. Technical Standards Analysis: JIS Norms and Transmission Chain Specifications
The precision and reliability of the JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain are not matters of chance, but the result of strict adherence to quantifiable engineering mandates. These mandates, primarily found within the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS), govern every aspect of the chain's design and manufacture.
A. Core Standard Interpretation (JIS Standard Chain)
A JIS Standard Chain is one that conforms to specifications like JIS B 1801, which details the dimensions, material grades, and testing methods for roller chains. This adherence is crucial because it ensures that a chain from any compliant manufacturer will perform identically and can be reliably interchanged in a drive system designed for that standard.
1. Dimensional Uniformity:
The JIS standard sets tight tolerances for key components, including the thickness of link plates and the diameter of the pins and bushings. This uniformity minimizes variations in chain length and pitch consistency, which is fundamental to maintaining proper engagement with sprockets and achieving smooth, low-vibration power transmission.
2. Material Integrity:
The standard specifies the minimum quality and heat-treatment requirements for the steel used in components like pins, bushings, and rollers. This guarantees the chain possesses the necessary core strength and surface hardness to withstand continuous, high-stress, and abrasive industrial environments.
B. Critical Parameters (Transmission Chain Specifications)
The performance of any JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain is defined by its core Transmission Chain Specifications. These parameters are non-negotiable and dictate the chain's compatibility and capacity.
1. Pitch (P):
This is the distance between the centers of adjacent pins. It is the most fundamental dimension and determines the size of the sprocket required. JIS standards define these pitches precisely, ensuring the chain engages smoothly with the teeth.
2. Roller Diameter (d1):
The diameter of the roller must be correct to ensure that the load is distributed evenly across the sprocket tooth profile, minimizing localized wear and maximizing component life.
3. Inner Plate Width (W):
Also known as the pitch between inner plates, this dimension dictates the clearance for the sprocket tooth and is vital for preventing binding.
These specifications collectively ensure that the chain is not only strong but also dimensionally perfect for its intended application, leading to highly efficient mechanical drive systems.
C. Strength and Fatigue Life
Beyond static dimensions, JIS standards rigorously define the limits of a chain's endurance. This focus on performance metrics is what distinguishes a quality JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain.
1. Minimum Tensile Strength:
This is the minimum static load a chain must be able to withstand before fracture. It is the ultimate measure of the chain's structural integrity, designed to prevent catastrophic failure under overload conditions.
2. Maximum Allowable Tension (Fatigue Limit):
This is perhaps the more critical measure for long-term industrial use. It represents the maximum dynamic load the chain can repeatedly bear (often millions of cycles) without suffering fatigue failure in the side plates or other components. Adherence to this limit is essential for ensuring a predictable and long operational lifespan.
D. Specification Comparison: Key Roller Chain Parameters (Illustrative)
The table below illustrates how specific dimensions are standardized across different pitch sizes for a common series of JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain (Roller Type):
| JIS Chain Series | Pitch (P) | Roller Diameter (d1) | Inner Plate Width (W) | Minimum Tensile Strength |
| 08B | 12.70 mm | 8.51 mm | 7.75 mm | 17.8 kN |
| 10B | 15.875 mm | 10.16 mm | 9.65 mm | 25.0 kN |
| 12B | 19.05 mm | 11.91 mm | 11.68 mm | 35.5 kN |
| 16B | 25.40 mm | 15.88 mm | 17.02 mm | 71.0 kN |
| 20B | 31.75 mm | 19.05 mm | 19.56 mm | 112.0 kN |
*Note: These values represent general JIS B series specifications and demonstrate the precise dimensional steps mandated by the Japanese Standard for various sizes.*
III. Structure and Selection: Core Application Considerations Based on Roller Chain Selection
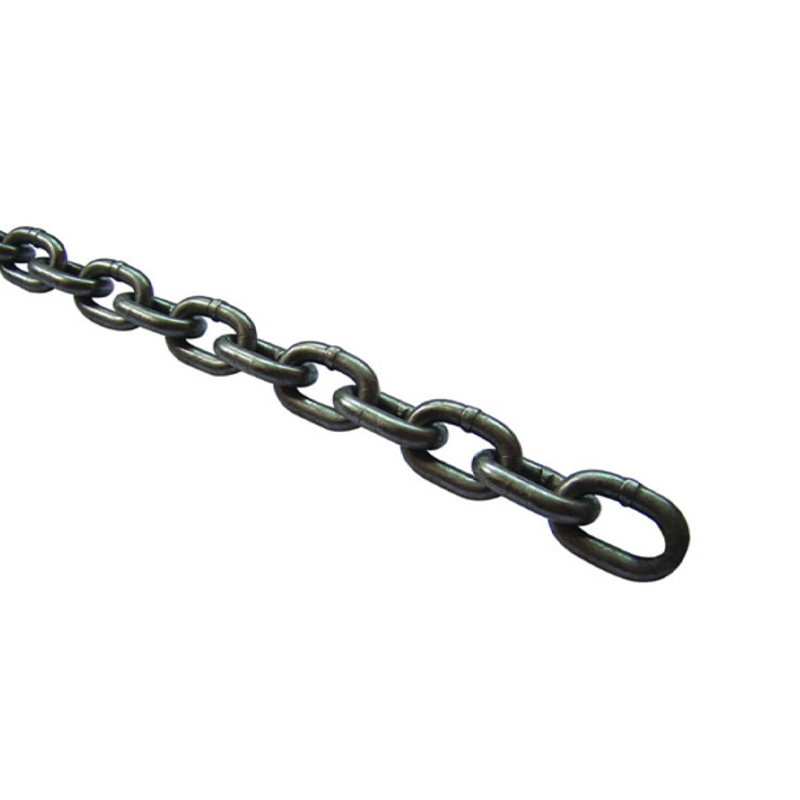
The JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain is fundamentally an assembly of precision-machined parts working in concert. Understanding its common structure, particularly the ubiquitous roller chain type, is essential for informed Roller Chain Selection and optimal performance in industrial applications.
A. Anatomical Analysis of the Typical Structure (Roller Chain Selection)
The standard roller link chain is composed of alternating inner and outer link plates connected by pins and bushings, which are shielded by rollers. This structural architecture enables the chain to efficiently handle both tensile loads and impact during meshing with sprockets.
1. Key Components and Function:
- Pins: These precision-ground components are press-fitted into the outer link plates and function as the load-bearing joints, enduring the highest shear stress.
- Bushings: Fitted between the inner link plates, bushings surround the pins, providing a wear-resistant surface against which the pins pivot.
- Rollers: These freely rotating components surround the bushings. They are crucial for reducing friction as the chain engages and disengages from the sprocket teeth, minimizing wear on both the chain and the sprocket itself.
- Link Plates: The inner and outer plates define the chain's tensile strength and overall length (pitch). The thickness and material quality of these plates, rigorously controlled by JIS standards, determine the chain's fatigue life.
B. Guidelines for Correct Selection
Effective application of a JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain requires more than matching the pitch; it necessitates a systematic approach to Roller Chain Selection based on operating conditions.
1. Load and Speed Factors:
Selection must first account for the required horsepower or torque to be transmitted, and the speed (RPM) of the driving shaft. These values are used with specific service factors (which account for shock loading and irregular power sources) to calculate the actual required strength.
2. Environmental Factors:
Conditions such as temperature, dust, moisture, or chemical exposure drastically influence the choice of chain series, lubrication, and material. Selecting a chain with insufficient protection against environmental contaminants is a common cause of premature failure.
C. Specialized Requirements (Stainless Steel Transmission Chain)
For applications demanding exceptional cleanliness or resistance to corrosion, a specialized Stainless Steel Transmission Chain is indispensable. This is a critical factor in Roller Chain Selection for specific industries.
1. Corrosion Resistance:
Standard carbon steel chains are prone to rust when exposed to moisture, mild acids, or cleaning solutions. Stainless Steel Transmission Chain (often Grade 304 or 316) provides the necessary inertness, making it mandatory for food processing, pharmaceuticals, and certain chemical industries where hygiene and non-contamination are paramount.
2. Operating Environment:
While stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance, it generally possesses a lower maximum allowable tensile strength than equivalent-sized carbon steel chains. Therefore, JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain selection in these high-corrosion environments requires a careful balance between material properties (stainless steel) and the required strength capacity, often necessitating a larger pitch size to achieve the necessary tensile rating.
3. Cleanliness and Maintenance:
The stainless-steel option often requires less frequent or specialized lubrication, simplifying maintenance protocols and adhering to stringent hygiene regulations typical of the food and beverage sectors.
IV. Application Fields and Value: Broad Industrial Chain Applications of Japanese Standard Chains
The rigorous engineering and quality control inherent in the JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain make it a preferred component across numerous high-demand industrial sectors. Its adherence to the precise JIS specifications ensures it performs reliably where component failure would lead to costly downtime and maintenance.
A. Diverse Application Scenarios (Industrial Chain Applications)
The versatility of the JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain is demonstrated by its wide range of Industrial Chain Applications. It serves as a vital component in synchronized motion and heavy-duty transfer systems globally.
1. Automation and Robotics:
In automated assembly lines and specialized machinery, precision is paramount. The consistent pitch accuracy and minimal dimensional variation mandated by the JIS standard allow the chain to maintain critical synchronization between various machine modules, ensuring flawless, high-speed operation in robotics and CNC applications.
2. Packaging and Printing Machinery:
These sectors require smooth, quiet operation at high speeds. The refined design of the JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain, including highly concentric rollers, reduces dynamic friction and noise, leading to improved performance stability during rapid cycling processes common in modern packaging equipment.
3. Material Handling and Conveyance:
For systems moving heavy items or operating over long distances (such as in warehousing or large manufacturing facilities), the high fatigue limit specified by the JIS standard is essential. This strength guarantees the chain can sustain continuous tension and thousands of operational cycles without premature wear or failure.
B. Defining the Value Proposition
The true return on investment from using a high-quality JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain is reflected in its operational excellence and longevity, which translates directly into lower life-cycle costs for the equipment owner.
1. High Precision and Efficiency:
Adherence to the strict JIS dimensional tolerances minimizes the "polygon effect" (vibrations caused by the chain entering the sprocket), resulting in smoother running, reduced noise levels, and less energy lost to friction. This high mechanical efficiency is a key operational value.
2. Extended Maintenance Cycles:
The superior materials and controlled heat treatment processes ensure components are highly resistant to abrasive wear. This extended wear life means less frequent replacement, reduced downtime for maintenance, and lower labor costs over the machine's lifespan. The reliability of the Japanese standard chain allows manufacturers to schedule maintenance preventatively, rather than reactively addressing failures.
3. Safety and Reliability:
In critical applications, the guaranteed Minimum Tensile Strength and Maximum Allowable Tension provide an essential safety margin, ensuring compliance with industrial safety protocols and protecting expensive machinery from the severe damage that can result from a catastrophic chain failure.
C. Conclusion and Outlook
The JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain occupies an indispensable position in the world of mechanical power transmission. Its strength is not just physical, but systemic, derived from the rigid JIS standard chain specifications that govern its production. As the global push toward greater automation, higher operating speeds, and more complex manufacturing processes continues, the demand for components with guaranteed precision, like the Japanese standard chain, will only increase. This chain's proven ability to deliver high precision, long life, and reliable performance ensures its ongoing relevance and evolution within the industrial drive sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the primary advantage of choosing a JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain over a chain adhering only to basic international standards?
A: The main advantage lies in the precision and stringent fatigue limits mandated by the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS). While international standards provide a baseline, the JIS standard sets tighter tolerances for key dimensions like pitch and roller diameter, ensuring higher precision in Transmission Chain Specifications. More critically, JIS defines robust criteria for Minimum Tensile Strength and Maximum Allowable Tension (fatigue limit). This rigorous compliance translates directly into smoother operation, reduced noise, increased reliability, and a significantly longer maintenance cycle in demanding Industrial Chain Applications.
Q2: Why is the choice of material, such as Stainless Steel Transmission Chain, so important for the overall longevity of the drive system?
A: Material choice is crucial because it dictates the chain's resistance to environmental factors, which are often the true cause of premature failure. A standard carbon steel chain is strong but vulnerable to rust and corrosion in damp, chemical, or wash-down environments (common in food processing or coastal operations). In these cases, a Stainless Steel Transmission Chain is selected, offering superior corrosion resistance even though it may have a slightly lower initial tensile strength than its carbon steel counterpart. The correct Roller Chain Selection balances the required load capacity against the operational environment to maximize the chain's service life and prevent costly system contamination or failure.
Q3: Where are chains and similar precision machinery components, such as the JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain, typically sourced, and what manufacturing quality should be expected?
A: Precision machinery components are sourced from specialized industrial suppliers focused on quality and technical standards. For example, a company like Shanghai TCH Metals & Machinery Co., Ltd. is a leading company specializing in the manufacturing and distribution of a diverse range of top-quality products, including chains, rigging hardware, and machinery parts. Established in 2001, their commitment to product excellence is backed by a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility and adherence to global quality practices. This strong focus on quality and innovation ensures that components like the JAP Japanese Standard Link Chain are manufactured to the highest standards, maintaining dimensional accuracy and reliability required for global industrial markets, including North America, Europe, and Japan.


 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語