Are Heavy Duty Stainless Steel Snap Hooks the Ultimate Solution for Extreme Environments?
Introduction to the Workhorse of Connectivity
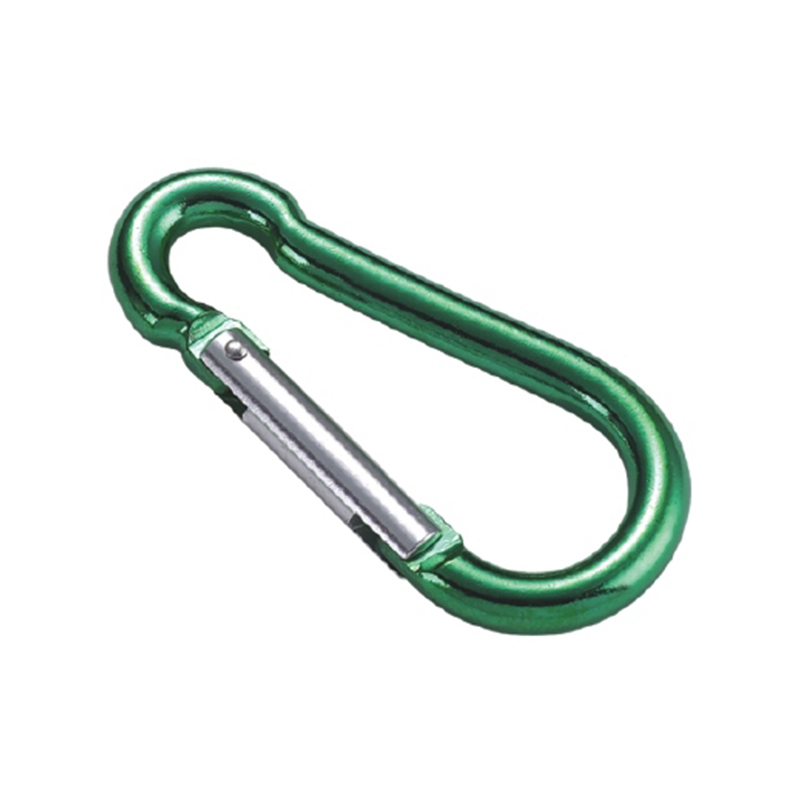
In the vast and demanding world of industrial hardware and marine applications, few components are as critical yet understated as the heavy duty stainless steel snap hook. This seemingly simple device is an engineering marvel, designed to bear immense loads, resist relentless corrosion, and provide fail-safe security in the most extreme conditions on Earth and at sea. But what exactly sets it apart from its lesser counterparts? The answer lies in a profound understanding of metallurgy, mechanical design, and environmental science. This article delves deep into the scientific and practical reasons why this specific type of connector has become the gold standard across countless industries, exploring the material properties, design intricacies, and rigorous testing that define its unparalleled performance.
The Unyielding Material: Why Stainless Steel Reigns Supreme
The core of the heavy duty stainless steel snap hook's superiority begins with its material composition. Not all stainless steels are created equal. For heavy-duty applications, grades 316 and 304 are predominantly used, with Grade 316, also known as marine-grade stainless steel, offering the highest resistance.
The secret to stainless steel's corrosion resistance is a passive chromium oxide layer that forms on its surface when exposed to oxygen. This layer is incredibly thin, invisible, and self-repairing. If scratched or damaged, the chromium reacts with moisture and oxygen in the air to reform the protective barrier. This is a crucial scientific property for a snap hook exposed to salt spray, chemicals, or abrasive environments.
Heavy duty versions require a high nickel and molybdenum content, particularly in 316 steel. Molybdenum drastically enhances resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion caused by chloride ions—the primary aggressor in seawater and de-icing salts. The term “heavy duty” also implies a thicker gauge of steel used in its construction, directly contributing to its higher Working Load Limit (WLL) and ultimate breaking strength. The material's high tensile strength ensures it deforms elastically under load, returning to its original shape without permanent damage, up to its designed limit.
Anatomy of Strength: Deconstructing the Design
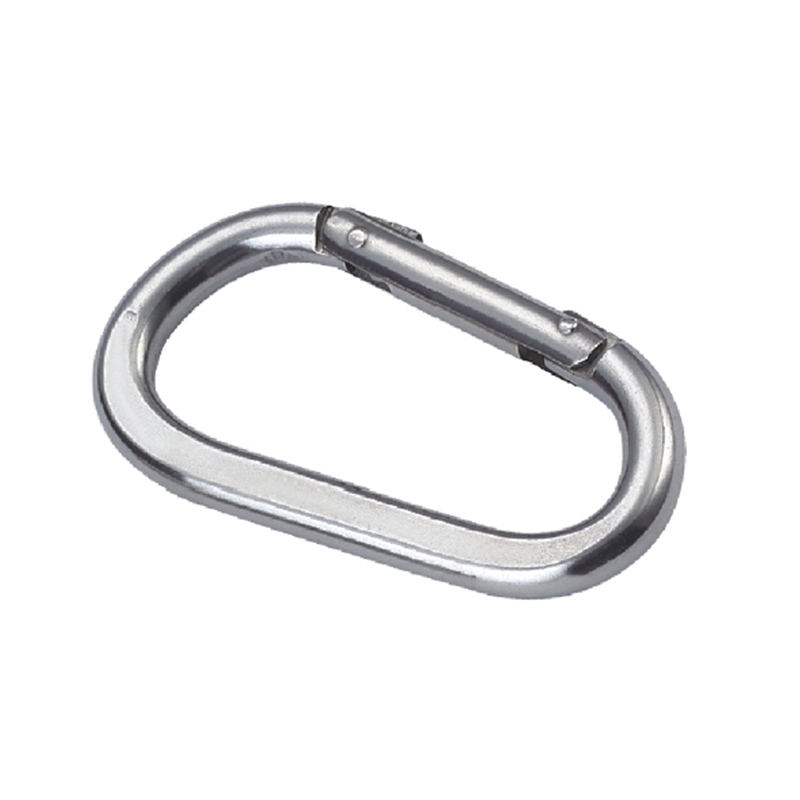
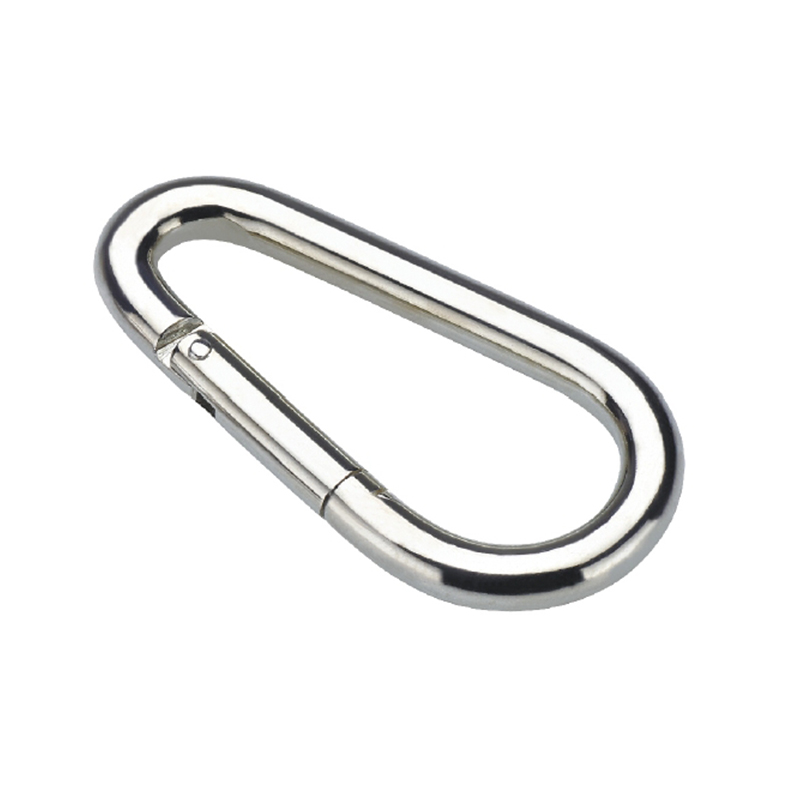
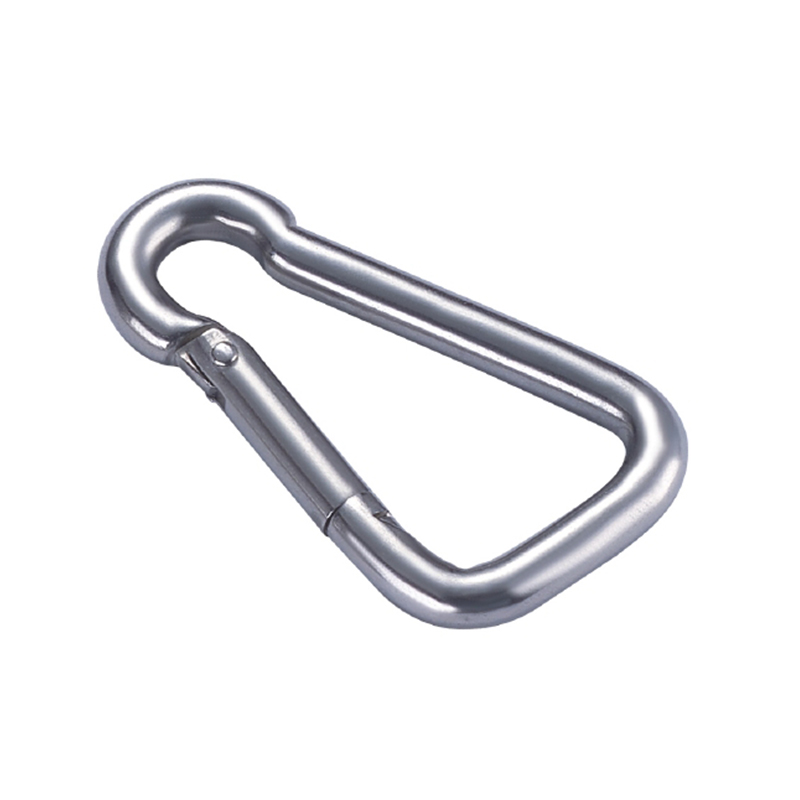
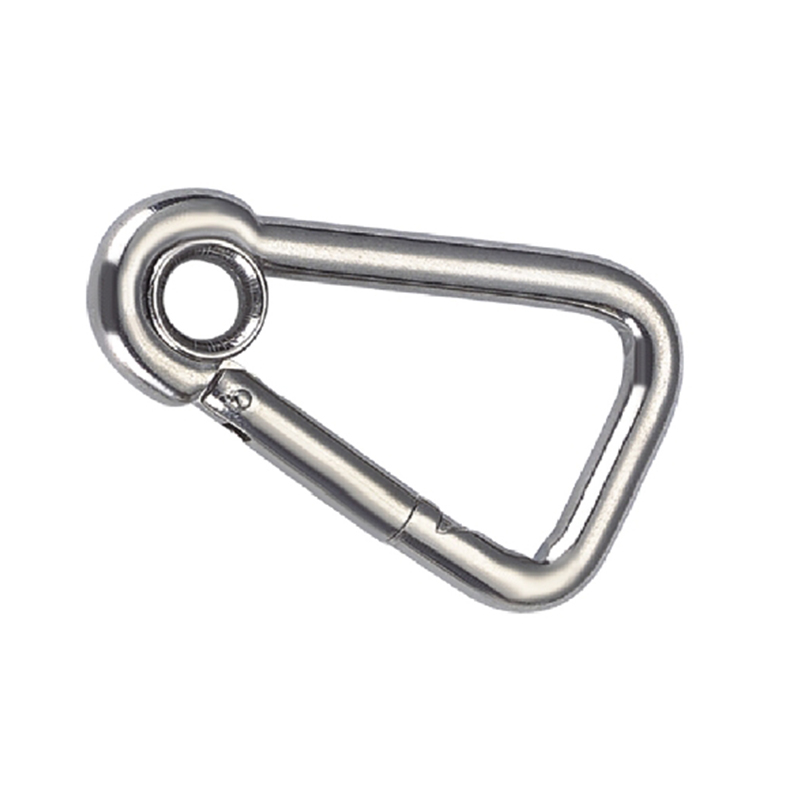
A heavy duty stainless steel snap hook is far more than a bent piece of metal with a gate. Its design is a meticulous exercise in physics and mechanical engineering to distribute stress and prevent failure.
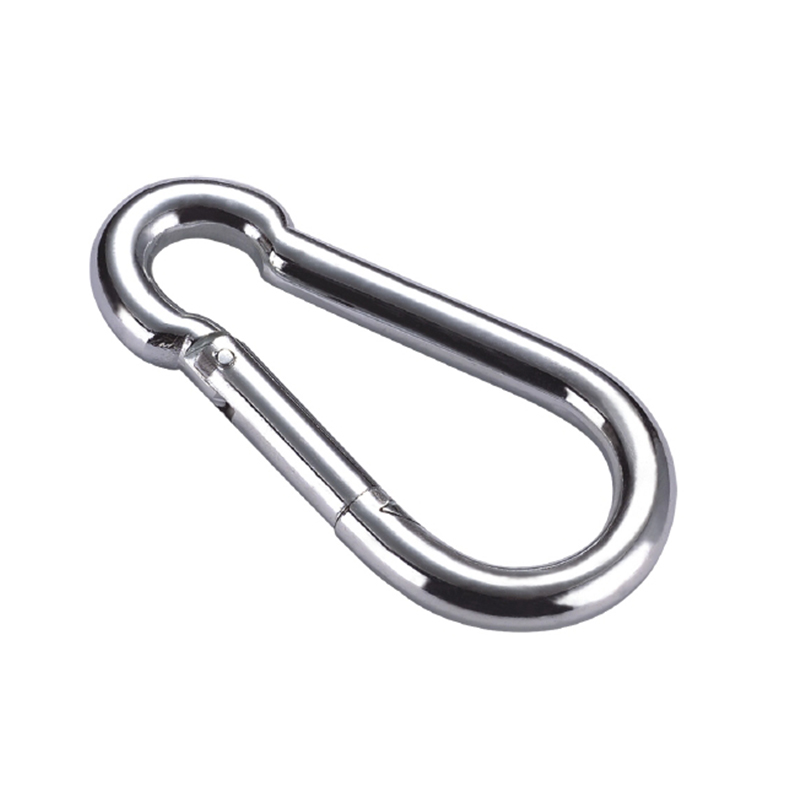
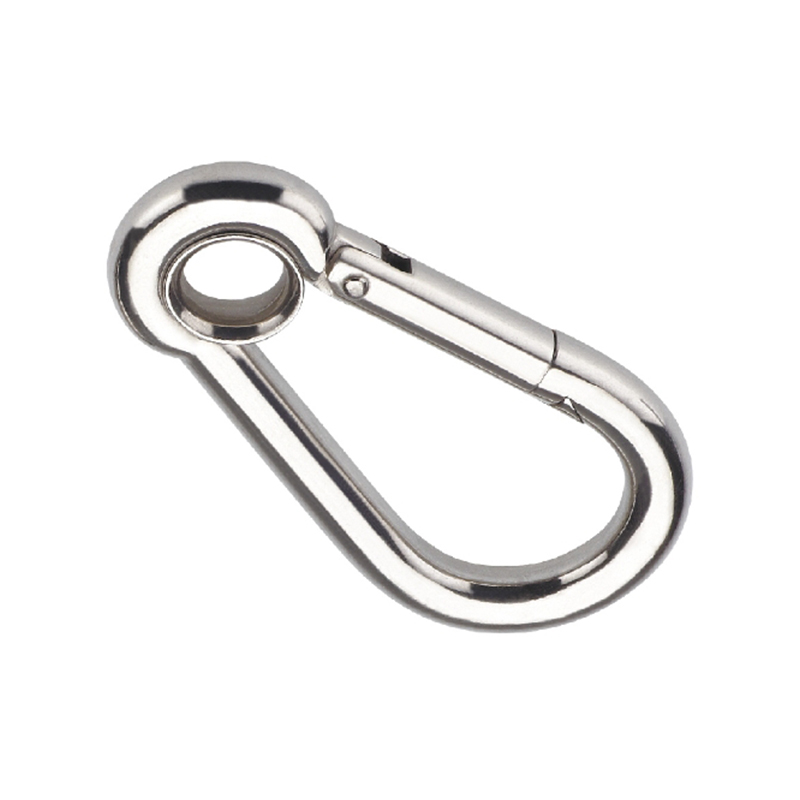
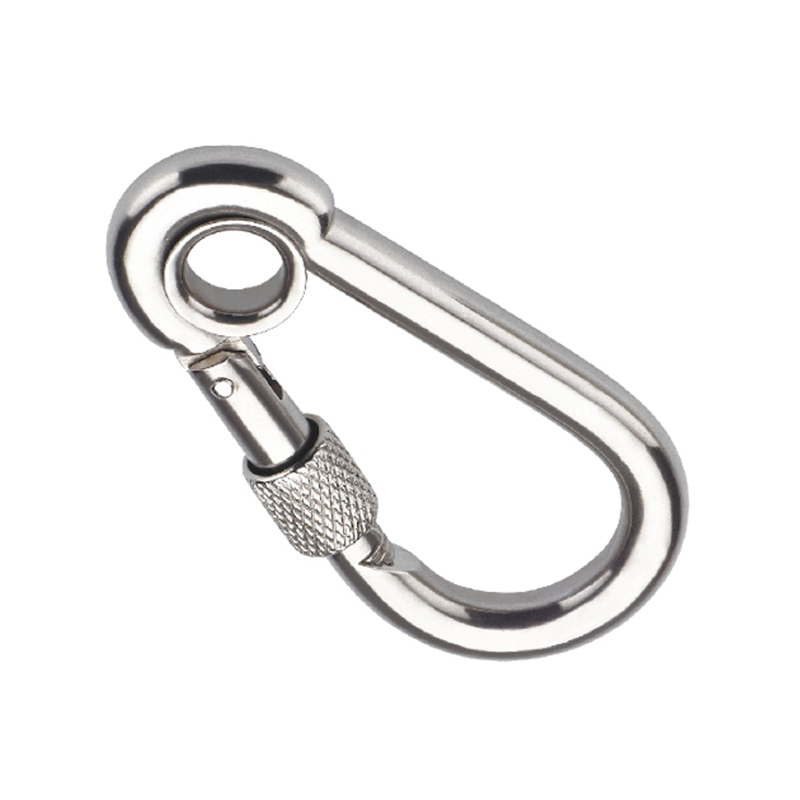
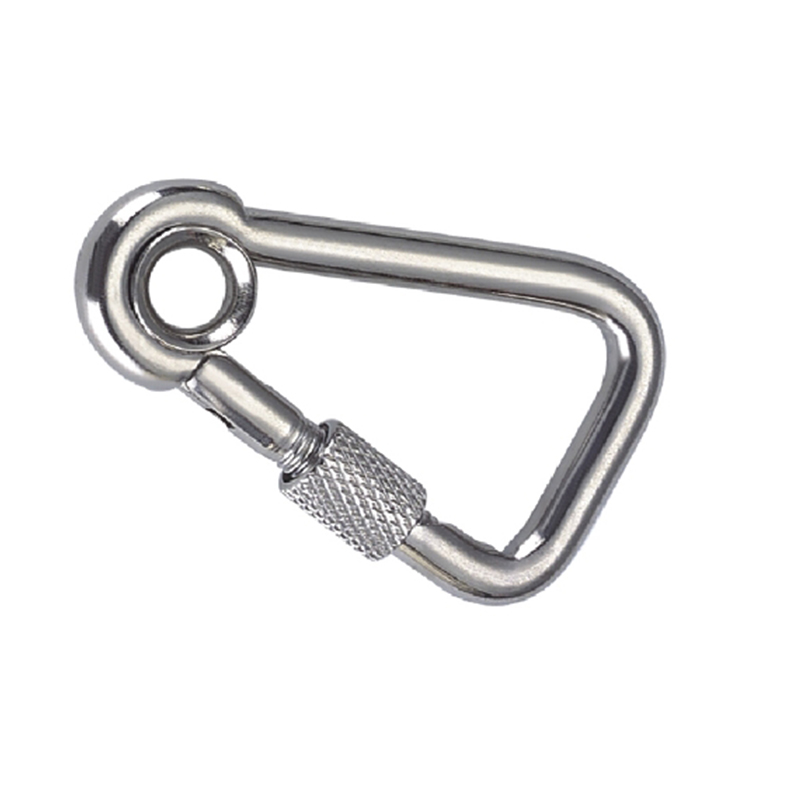
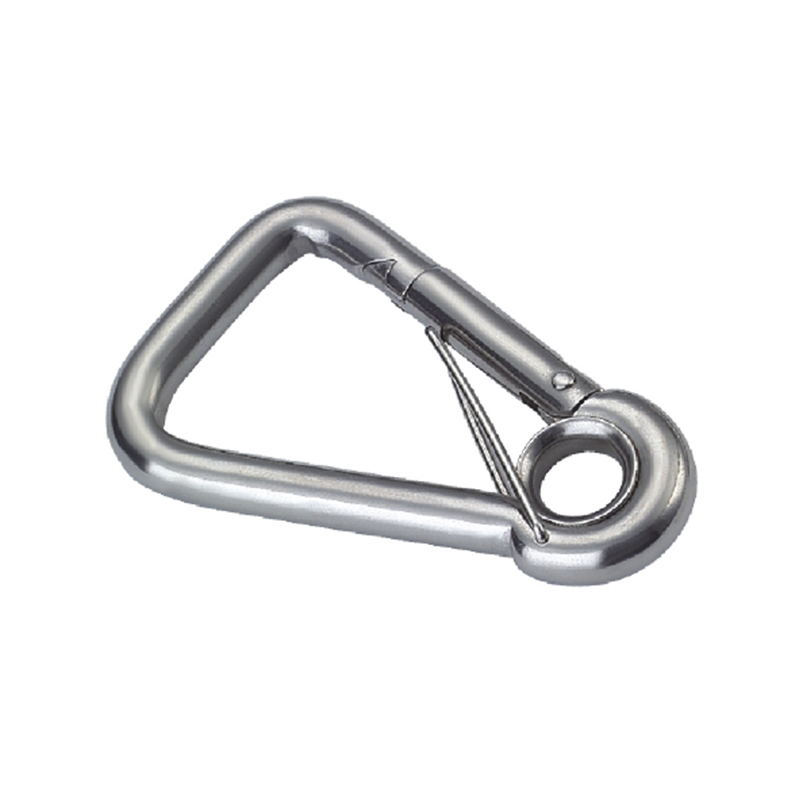
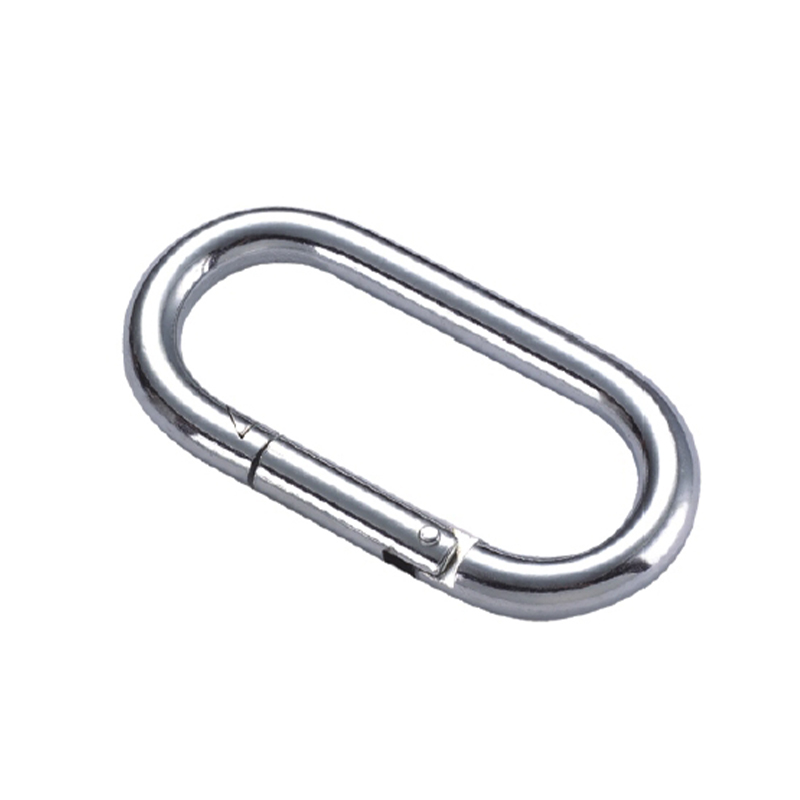
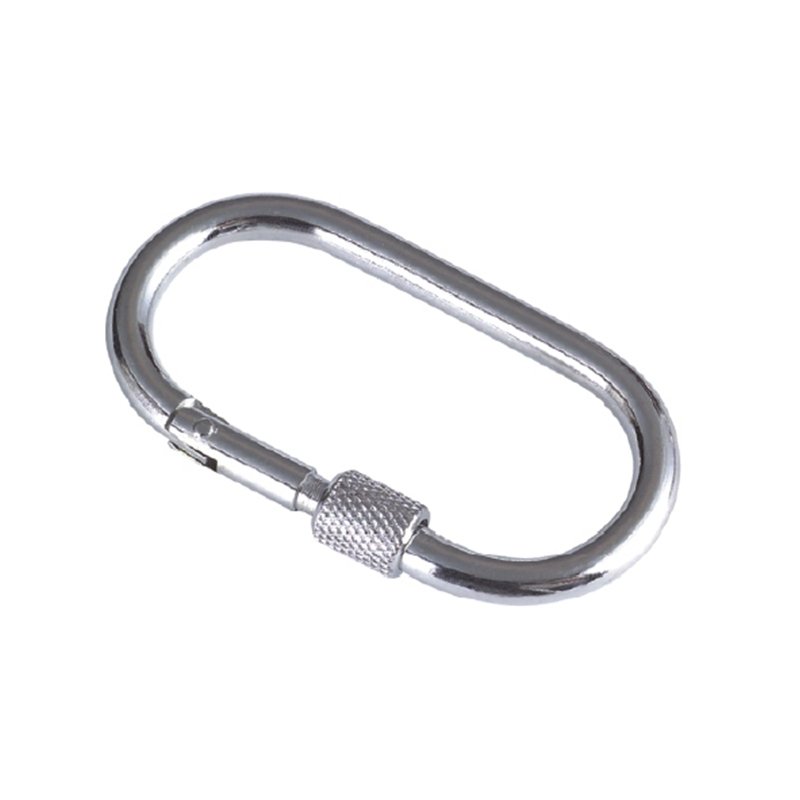
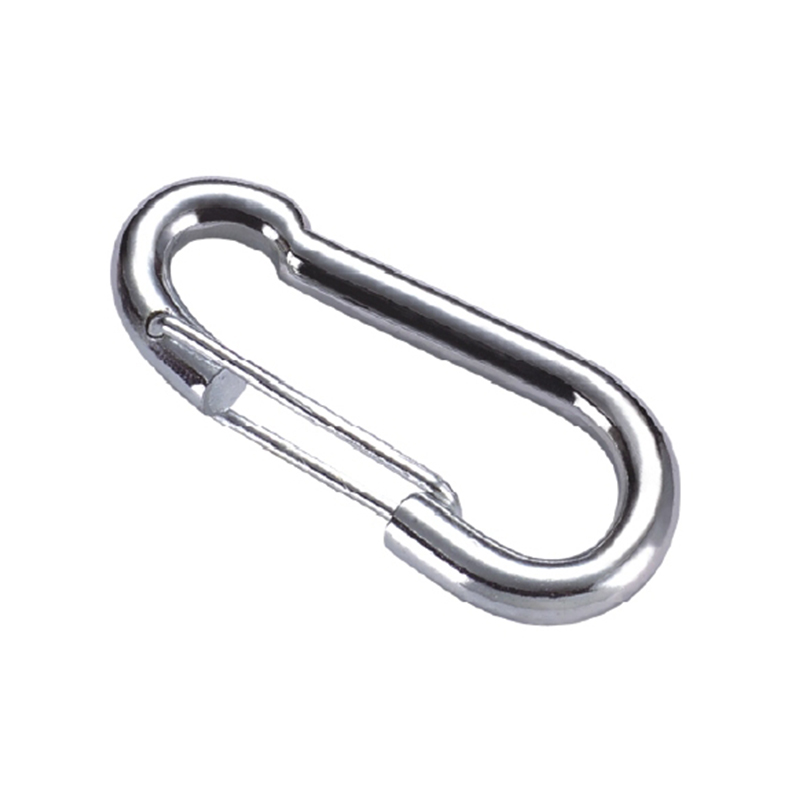
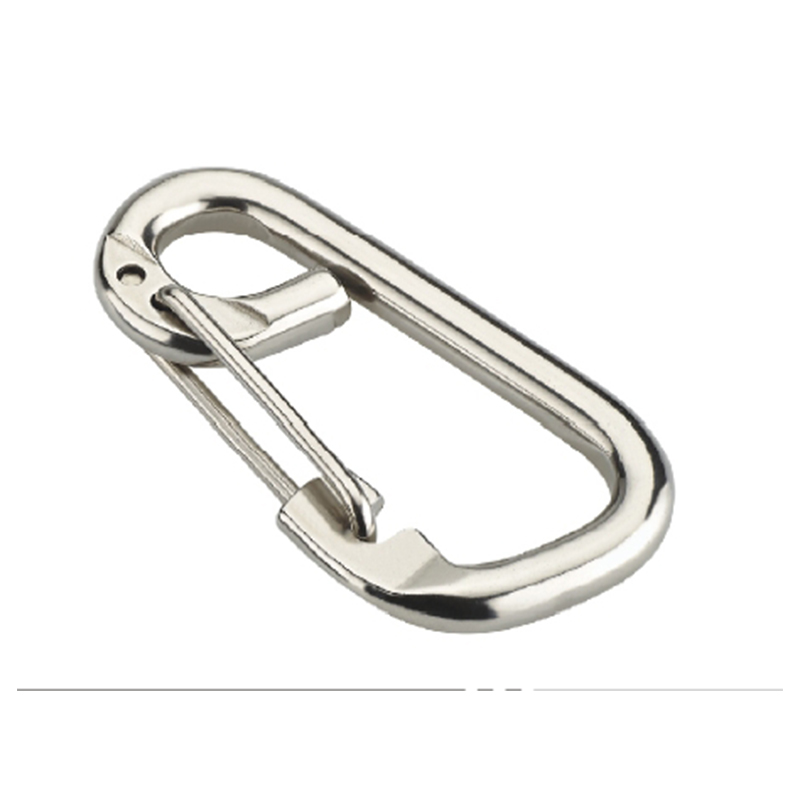
The most critical area is the nose of the hook. On a quality heavy duty snap hook, the nose is designed with a generous radius, avoiding sharp angles that create stress concentration points. Stress concentration is a phenomenon where force becomes focused on a tiny area, dramatically increasing the likelihood of metal fatigue and catastrophic failure. The smooth, rounded contour ensures that loads are distributed evenly along the curve of the hook, aligning with the fundamental principles of how forces act on a curved beam.
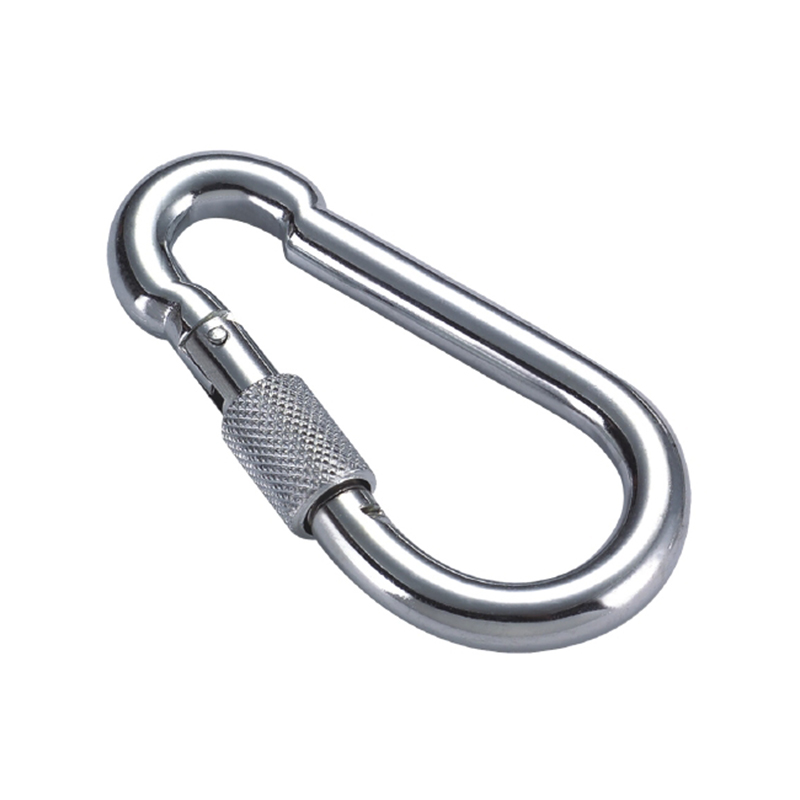
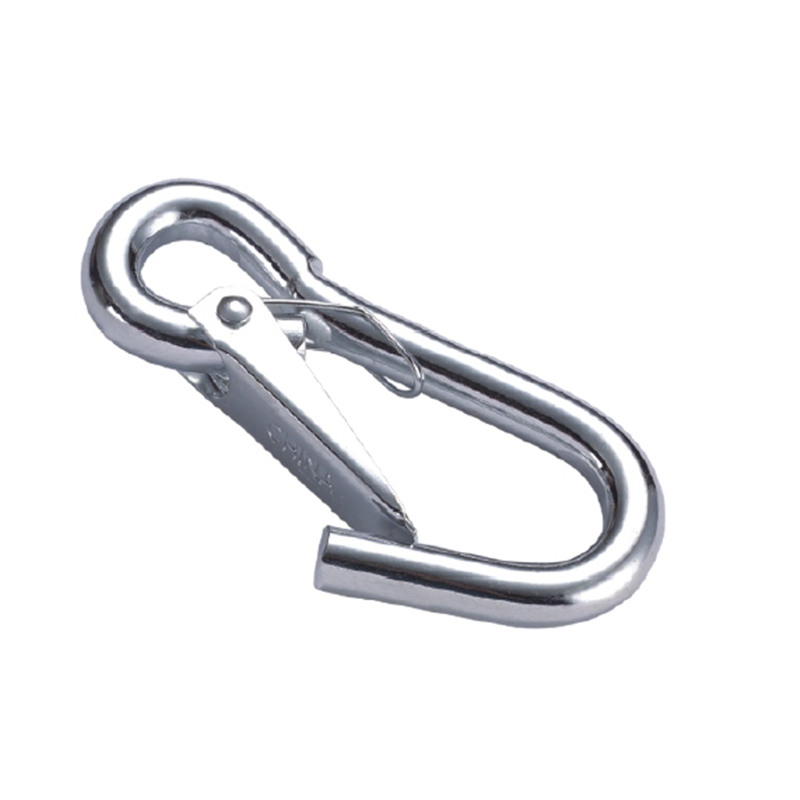
The gate mechanism is another masterpiece of engineering. It must operate smoothly under load yet be utterly secure. Most heavy-duty models employ a double-locking or triple-locking mechanism. This often involves a spring-loaded sleeve that must be manually pulled back before the gate can be opened. This positive locking action prevents “roll-out,” where the gate could accidentally open if twisted against a hard point. The spring itself is typically made from a stainless steel alloy capable of millions of cycles without losing its tension, a property known as high fatigue resistance.
Furthermore, the pivot point of the gate is reinforced with a stout rivet or pin, which is often mechanically pressed or welded in place to eliminate any risk of dislodgement. The entire assembly is designed to have minimal play or wiggle, ensuring that under load, the force is transferred through the body of the hook and not onto the moving parts of the gate.
Rigors of Validation: How Heavy Duty Snap Hooks Are Tested
Before a heavy duty stainless steel snap hook ever reaches a job site, it undergoes a battery of brutal tests to certify its ratings. These tests are governed by international standards set by organizations like ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) and OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration).
The most fundamental test is the Destructive Break Test. A sample hook is placed in a tensile testing machine and pulled apart until it fails. The force required to break it must significantly exceed its stated Ultimate Breaking Strength (often 5 times its Working Load Limit). This ensures a massive safety margin.
Cycle Testing is another critical validation. The gate mechanism is opened and closed tens of thousands of times—often by a automated machine—to simulate years of use. After this fatigue test, the hook must still meet all its load-bearing specifications without any deformation or malfunction of the gate.
Corrosion testing involves placing samples in salt spray chambers for hundreds of hours. This accelerated environment simulates years of exposure to marine conditions. After testing, the hook must show only superficial discoloration with no pitting corrosion that could compromise its structural integrity. Metallurgical analysis is also conducted to verify the exact chemical composition and ensure the material meets the required grade standards.
Beyond the Obvious: Diverse Applications
While marine and construction are obvious homes for the heavy duty stainless steel snap hook, its applications are remarkably diverse. In theatrical rigging, they secure lighting, speakers, and scenery high above stages, where failure is not an option. In forestry and arboriculture, they connect climbers to life-support systems. In adventure sports like rock climbing and caving (though specialized climbing carabiners are used for primary protection), they find use in gear loops and equipment hauling. In transportation and logistics, they secure cargo on trucks and ships, enduring constant vibration and weather exposure. In every case, the combination of immense strength and corrosion resistance makes it the indispensable link.
The global demand for such reliable hardware has fostered a specialized manufacturing sector focused on precision and quality. In China, a hub for industrial production, companies like Shanghai TCH Metals & Machinery Co., Ltd. have developed extensive expertise in metallurgy and forging processes. Their work in supplying high-grade components to the international market involves adhering to strict quality control protocols, ensuring that every heavy duty stainless steel snap hook that leaves their facility meets the rigorous demands of global safety standards and performs flawlessly in the field. This focus on material science and manufacturing excellence is what allows industries worldwide to operate with confidence in harsh environments.
Selecting the Right Tool for the Job
Choosing a heavy duty snap hook is not a trivial task. It requires careful consideration of the Working Load Limit, which must be appropriate for the application with a sufficient safety factor. The environment is the next critical factor; Grade 316 is essential for any marine or chemical exposure, while 304 may suffice for general outdoor use. The gate mechanism must be inspected for ease of use with gloves and its positive locking action. Finally, certification marks from recognized bodies are non-negotiable for any life-safety or critical load-bearing application. It is this intricate interplay of science, engineering, and diligent selection that makes the heavy duty stainless steel snap hook a masterpiece of functional design.

 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語