Introduction
Maintaining rigging hardware is essential for ensuring both the longevity of the equipment and the safety of operators. Rigging hardware is critical in industries like construction, marine operations, and heavy lifting, where safety is paramount. Proper care and maintenance practices can prevent accidents, prolong the service life of components like quick links, shackles, and hoists, and reduce operational costs.
The Importance of Rigging Hardware Maintenance
Rigging hardware includes a wide range of components such as quick links, shackles, wire ropes, hoists, and slings. These components are subjected to high-stress environments, exposure to various elements, and heavy loads. If not maintained properly, these components can wear out, leading to malfunctions, accidents, and even catastrophic failures. Proper maintenance reduces the likelihood of such occurrences, ensuring not only the safety of workers but also the efficient functioning of lifting operations.
Types of Rigging Hardware and Their Common Issues
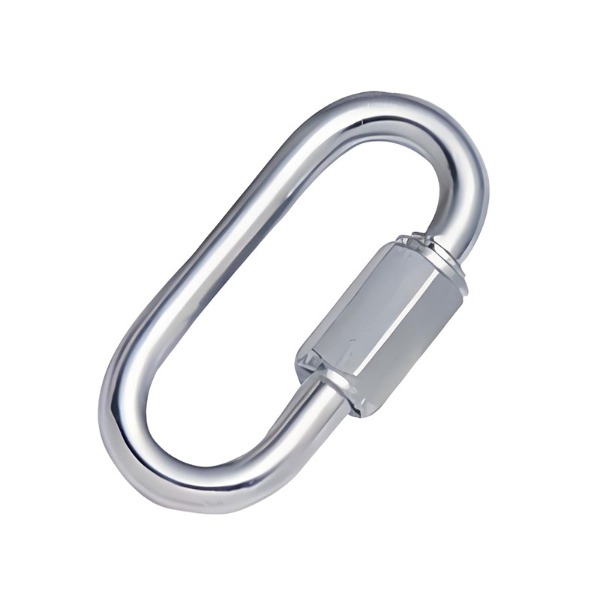
Quick Links
Quick links are often used to connect different rigging components together. They are reliable and simple to use but can suffer from wear and corrosion if not maintained correctly.
Common issues:
- Rusting and corrosion due to prolonged exposure to moisture
- Wear and tear from frequent use
- Improper closure leading to weak connections
Shackles
Shackles are designed to connect lifting slings to lifting loads. They are widely used in various applications such as construction and marine lifting.
Common issues:
- Corrosion due to exposure to harsh environments
- Overloading and deformation of the shackle pin
- Wear from repeated loading and unloading
Wire Ropes
Wire ropes are an essential component of many rigging setups, often used in hoisting or lifting heavy loads.
Common issues:
- Kinking or bending of the wire rope
- Fraying and wear due to friction or abrasive surfaces
- Corrosion from exposure to saltwater or chemicals
Hoists and Slings
Hoists and slings are integral parts of lifting operations and require consistent inspection and maintenance to ensure their safety.
Common issues:
- Malfunctioning hoist mechanisms
- Wear and tear on sling fibers
- Misalignment of pulleys leading to undue stress on the rigging hardware
Key Maintenance Practices for Rigging Hardware
Regular Inspection
Routine inspection is the first step in identifying wear and damage before it becomes a safety hazard. Every rigging component should be checked for visible signs of corrosion, wear, or deformation. Critical points to inspect include:
- Check for cracks, rust, or corrosion.
- Look for deformations, especially on shackles and quick links.
- Inspect slings for fraying or cuts.
- Check hoists and ropes for signs of malfunction.
Lubrication
Lubrication plays a significant role in ensuring smooth movement and reducing friction between moving parts. Proper lubrication of quick links, shackles, and hoists can prevent wear and reduce the risk of failure.
Lubrication steps:
- Use appropriate lubricants for specific components (e.g., grease for shackles, oil for hoist mechanisms).
- Regularly clean components before applying lubricant to prevent dirt buildup.
- Ensure lubrication is applied in all moving parts, including pins and shackles.
Cleaning and Removal of Corrosion
Cleaning rigging hardware regularly helps remove dirt, debris, and corrosive substances. For metal components, removing any corrosion before it spreads is vital for maintaining integrity.
Cleaning tips:
- Clean shackles and quick links with a wire brush or abrasive pad to remove surface corrosion.
- Use a mild detergent and water solution to clean all rigging components.
- Apply anti-corrosion coatings where necessary to prevent future rust formation.
Load Testing and Re-certification
Regular load testing ensures that the rigging hardware can handle the intended weight. This is particularly important for components like wire ropes and hoists, where the risk of failure increases under excessive load.
Load testing tips:
- Perform load tests periodically or after significant maintenance.
- Ensure all rigging hardware is certified for the appropriate load weight.
- Verify that all components are functioning properly under load conditions.
Proper Storage
Proper storage of rigging hardware when not in use can prevent premature wear. Hardware should be stored in a clean, dry, and protected environment to avoid damage from external elements.
Storage tips:
- Store rigging components in a dry, well-ventilated area.
- Keep hardware off the ground to prevent contact with moisture.
- Avoid stacking heavy loads on rigging components to prevent deformation.
Replace Worn or Damaged Parts
Even with the best maintenance practices, rigging hardware will eventually wear out. It is crucial to replace worn or damaged components immediately to prevent failure during lifting operations.
Replacement tips:
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for replacement intervals.
- Replace any components showing signs of extreme wear, such as bent pins, frayed ropes, or cracked shackles.
- Use original parts for replacement to maintain safety and performance standards.
Preventing Common Rigging Hardware Failures
By following the maintenance practices outlined above, you can significantly reduce the chances of rigging hardware failure. However, certain preventative measures can further enhance the longevity and safety of the hardware.
Preventative measures:
- Use anti-corrosion treatments to protect components from environmental elements.
- Avoid overloading rigging components beyond their rated capacity.
- Train personnel on proper usage and maintenance of rigging hardware to reduce the risk of misuse.
Conclusion
Maintaining rigging hardware, including quick links, shackles, hoists, and wire ropes, is crucial for ensuring both the longevity of the equipment and the safety of operations. Regular inspections, cleaning, lubrication, load testing, and proper storage practices all contribute to extending the lifespan of rigging hardware. By adhering to these best practices, companies can ensure their lifting operations remain efficient, safe, and cost-effective.
FAQ
Q1: How often should I inspect my rigging hardware?
A1: Rigging hardware should be inspected before every use and periodically during maintenance schedules to ensure safe operation.
Q2: Can I use any lubricant for rigging components?
A2: No, different components require specific lubricants. Always use the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure optimal performance.
Q3: What should I do if I find damaged rigging hardware?
A3: Damaged components should be immediately removed from service and replaced to prevent any safety hazards.
Q4: How can I prevent corrosion on rigging hardware?
A4: Regular cleaning, lubrication, and the use of anti-corrosion coatings can significantly reduce the likelihood of corrosion.
Q5: Is load testing necessary for all rigging hardware?
A5: Yes, regular load testing ensures that the hardware is functioning correctly and can safely handle the weight during operations.


 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語